
Exploring the Future of Smart Cities
What are Smart Cities?
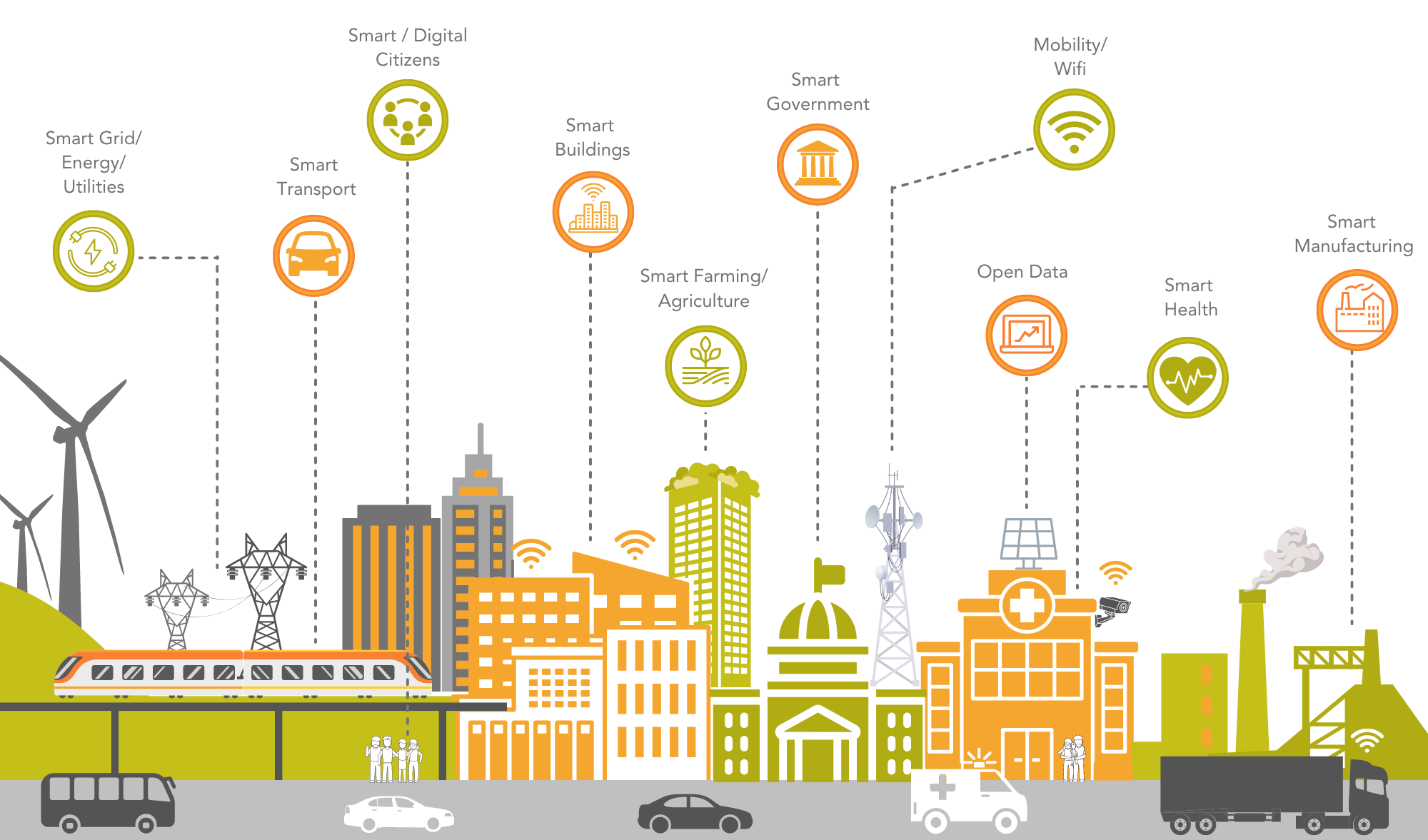
A smart city is one that collects data using various electronic methods and sensors. Insights derived from that data are utilised to efficiently manage assets, resources, and services; in turn, that data is used to improve operations throughout the city. Data collected from citizens, devices, buildings, and assets is then processed and analysed in order to monitor and manage traffic and transportation systems, power plants, utilities, water supply networks, waste, crime detection, information systems, schools, libraries, hospitals, and other community services.
The smart city concept integrates information and communication technology (ICT) with various physical devices linked to the Internet of Things (IoT) network to improve the efficiency of city operations and services and connect to residents. A smart city's major objective is to increase policy efficiency, decrease waste and inconvenience, improve social and economic quality, and optimise social inclusion.
Why Has Demand for Smart Cities Increased?
More than half of the world's population already live in cities. According to predictions, that figure will rise to two-thirds by 2050. This enormous change is ultimately due to the vast opportunities people have in cities to design their own lives. Increasing urbanisation, however, brings new challenges: as cities expand, people's needs and demands must be accommodated with as little environmental impact as possible.
Climate change is one of the most urgent concerns we face today. CO2 emissions must be reduced in the coming decades, and steps must be made to prevent global warming, floods, and protracted heat waves. Cities are responsible for over three-quarters of global greenhouse gas emissions. Being one of the biggest polluters, government and the construction industry are expected to find solutions.
Smart City Goals
A smart city's primary purpose is to develop an urban environment that provides its residents with a high quality of life while simultaneously creating overall economic growth. As a result, one important advantage of smart cities is their capacity to facilitate increased service delivery to inhabitants while using less infrastructure and money. When the population of cities grows, it becomes vital for these cities to handle the growing population by making better use of its infrastructure and assets. Smart city applications can enable these advancements, promote city operations, and improve residents' quality of life.
Successful smart cities follow four steps:
- Collection: Smart sensors installed across the city collect data in real time.
- Analysis: Data acquired by smart sensors is analysed to get valuable insights.
- Communication: The findings from the analysis are presented to decision makers via strong communication networks.
- Action: Cities use the insights pulled from the data to create solutions, optimize operations and asset management, and improve the quality of life for residents.
Key Features of a Smart City
- Encouraging mixed land use in area-based developments comprising a variety of appropriate activities and land uses close to one another to optimise land usage.
- Housing and inclusion - increase housing opportunities for all.
- Maintaining and developing open spaces - parks, playgrounds, and recreational areas - to improve inhabitants' quality of life, reduce urban heat effects on areas, and promote overall eco-balance.
- Building walkable communities reduces congestion, air pollution, and resource depletion while also boosting the local economy, encouraging relationships, and ensuring security. The road network is built or renovated to accommodate not just vehicles and public transportation, but also pedestrians and cyclists.
- Using Smart Solutions to improve infrastructure and services in area-based development.
The core infrastructure elements of a Smart City
- Guaranteed electrical supply.
- Sufficient water supply.
- Affordable housing.
- High level of sustainability.
- Sanitation, including solid waste management.
- Efficient urban mobility and public transport.
- Suitable health and education facilities.
- Robust IT connectivity and digitalization.
- Effective governance, in particular e-Government and citizen participation.
- Safety and security of residents, particularly women, children and the elderly.
Summary
The future of our world is decided by the quality of its future cities; Cities house 54% of the world's population, which is predicted to climb to 66% by 2050, adding 2.5 billion people to the urban population during the next three decades. With this predicted population growth comes the need to manage environmental, social, and economic resource sustainability. This is becoming increasingly crucial considering future urban population expansion, which will necessitate more effective use of infrastructure and assets. Smart city services and applications will enable these developments, resulting in an improved quality of life for inhabitants. Smart city enhancements also add value to existing infrastructure by introducing new revenue sources and operational efficiencies that help governments and communities save money.
How Can We Help?
Searching for an opportunity in the construction industry? Or are you a hiring manager in search of the top talent in the market today? Contact our team of industry experts to start the conversation. getus@jamesgrayrecruitment.com

